World Hepatitis Day 2021: Here’s All About Its Symptoms, Causes And Detection

Every year on July 28, World Hepatitis Day brings the entire world together under one concept to raise awareness of the worldwide burden of viral hepatitis and to encourage positive change. The theme for 2021 is “Hepatitis Can’t-Wait.” It emphasizes the importance of efforts to eradicate hepatitis as a public health hazard by 2030. This campaign, with the tagline “Seek Hep. Seek Help. Get Tested Today” aims to promote awareness among people to get diagnosed and treated to lower the chance of liver cancer.
Types:
There are 5 types of Hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E, furthermore are classified into two categories:
- Acute Hepatitis
- Chronic Hepatitis
Acute Hepatitis: Acute viral hepatitis occasionally can develop into a severe form termed as “fulminant liver failure”. Because fulminant hepatitis seems to have an 80% death rate without liver transplantation. Viruses transmitted by blood and bodily fluids (Hepatitis B and C), unlike waterborne viruses, can cause rapid symptoms, but they are more likely to persist in the body for a decade or two and cause chronic hepatitis.
Chronic Hepatitis: The word “chronic hepatitis” means “long-lasting hepatitis.” Hepatitis B and C viruses produce continuous long-term hidden inflammation (Chronic Hepatitis) and scarring (fibrosis) in the liver due to the immune system’s inability to remove them. These procedures result in cirrhosis and liver cancer. The patient is asymptomatic when silent damage occurs in chronic hepatitis.
Hepatitis B and C together are the leading causes of death, claiming the lives of 1.3 million people each year. The majority of patients, on the other hand, have yet to be diagnosed and treated. Hepatitis B and C, if left untreated, are significant risk factors for liver cancer, the sixth largest cause of death.
Symptoms:
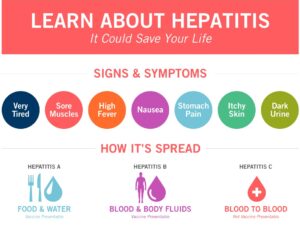
Flu-like symptoms, fatigue, dark urine, high fever, nausea, and yellowing of the skin and eyes are all indications of acute viral hepatitis. Infection with this virus, on the other hand, may appear with little symptoms or go unnoticed entirely.
Causes:
Hepatitis A and E are mostly transmitted by the ingestion of infected food and water. Hepatitis B, C, and D are most commonly contracted through coming into touch with contaminated blood or bodily fluids.
The “incubation phase” refers to the time between viral entry into the body and the onset of hepatitis. It varies depending on the virus. Hepatitis A and E viruses need two to six weeks to incubate, while Hepatitis B and C viruses take two to six months to incubate.
Detection:
Early detection and screening are crucial for conquering these viruses before they cause irreversible damage. Until undiagnosed persons in the silent phase are found and assigned to care, millions of people will continue to suffer and lives would be sacrificed.
According to the WHO’s research, immunization, diagnostic tests, medicines, and information campaigns can avert an estimated 4.5 million premature deaths in low- and middle-income countries by 2030. From 2016 to 2030, governments worldwide have adopted the WHO’s global hepatitis plan, which seeks to reduce new hepatitis infections by 90% and fatalities by 65%.